Some important information about Anaesthsia and your surgery:
Different types of Anaesthesia
|
General anaesthetic a state of controlled unconsciousness during which you feel nothing. You will have no memory of what happens while you are anaesthetised |
Local anaesthetic numbs a small part of the body. It is used when the nerves can be easily reached by drops, sprays, ointments or injections. Having teeth removed and some common operations on the eye often use local anaesthetic. You stay awake, but free from pain |
|
Spinal and epidural anaesthetic the most common regional anaesthetics. These injections can be used for operations on the lower body, such as Caesarean section, bladder operations, or replacing a hip. You stay awake, but free from pain |
Sedation involves using small amounts of anaesthetic medicines to produce a ‘sleep-like’ state. It makes you physically and mentally relaxed, but not unconscious. You will be free from pain. |
|
Regional anaesthetic medicine is injected near to the nerves which supply a larger or deeper area of the body. The area of the body affected becomes numb. You stay awake, but free from pain. |
Tell your Anaesthetist this important information...
It is important to tell your anaesthetist as much information about yourself as possible, including the following details:
- Every medical condition you have – even if it is well treated, no matter how big or small a problem it is for you: we need to know
- All medications that you are on. You will be able to continue taking most of these normally. There might be some special instructions for some types of medication
- Your weight and your level of fitness are very important to help your body manage the stresses associated with surgery, anaesthesia, and hospital admission.
- If you smoke, drink alcohol, or take any other recreational drugs.
What will the Anaesthetist do to start?
- Insert a thin plastic tube called an intravenous cannula into one of your veins, often on the back of your hand
- Attach monitors including a blood pressure cuff, heart monitor, and finger probe to measure your oxygen levels
- Give you oxygen from a clear face mask.
Most general anaesthetics are started by injecting medications through your cannula. You may feel slightly light-headed at first. As the medicine works you will become unconscious very quickly.
Sometimes you can breathe a mixture of anaesthetic gases and oxygen through the facemask to start. The gases smell quite strong, and it usually takes two or three minutes to become unconscious. This is most commonly done with children.
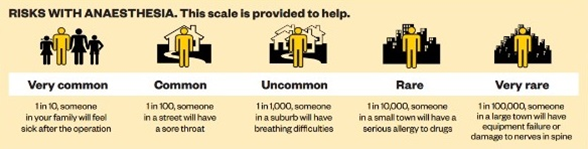
Are there any risks with Anaesthesia?
As with all medical processes, nothing is completely risk-free. Anaesthesia is very safe – the risk of death due only to anaesthetic causes is about 1: 130000. Anaesthetists are trained to prevent complications. They can treat them quickly if they happen.
Useful websites
These websites have useful additional information about anaesthesia: